Quantifying The Mass Political Ideology Using a Neural Network Architecture
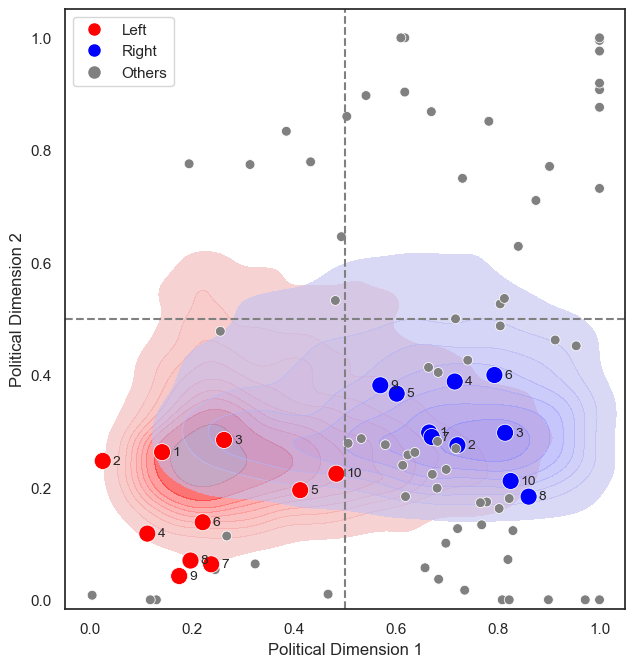
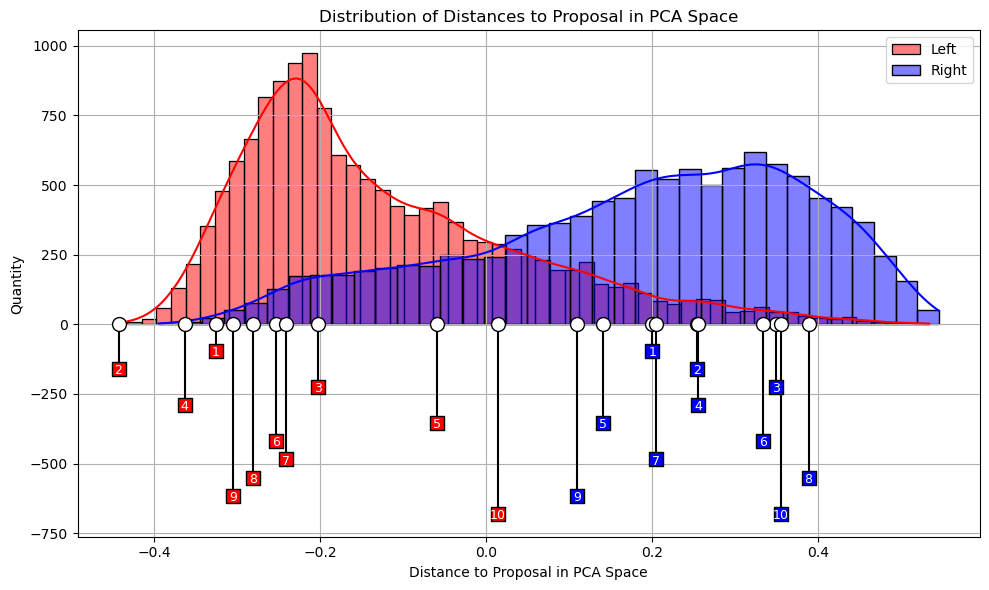
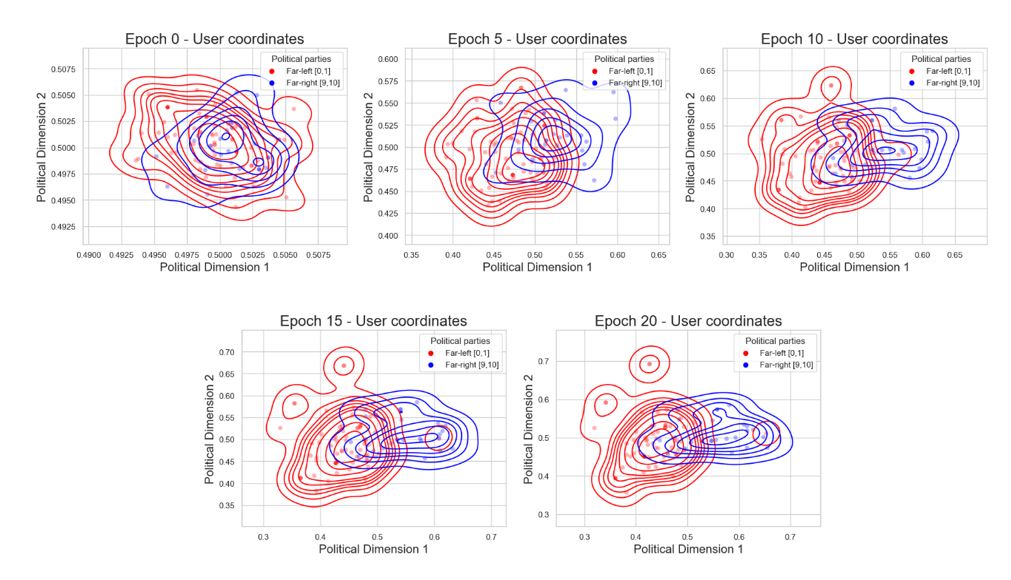
Developed a Neural Network algorithm to map political ideology and predict individual political positions and preferences within a political landscape (latent features) using representational learning techniques. This method involved creating a unique and innovative Neural Network architecture and was trained on over 6 million data points using Pairwise Comparison. This research enables the training of an autonomous voter system designed to predict individual political preferences based on their history, marking a significant step towards digital democracy. The development of the neural network algorithm contributes to state-of-the-art research in machine learning by advancing methods for ideological mapping and preference prediction.
Content-Based Tourist Destination Recommendation System
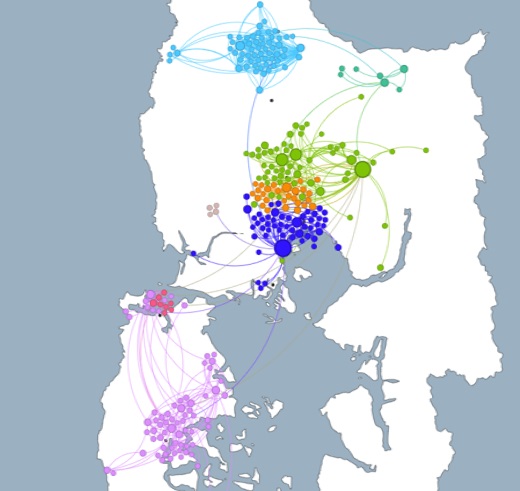
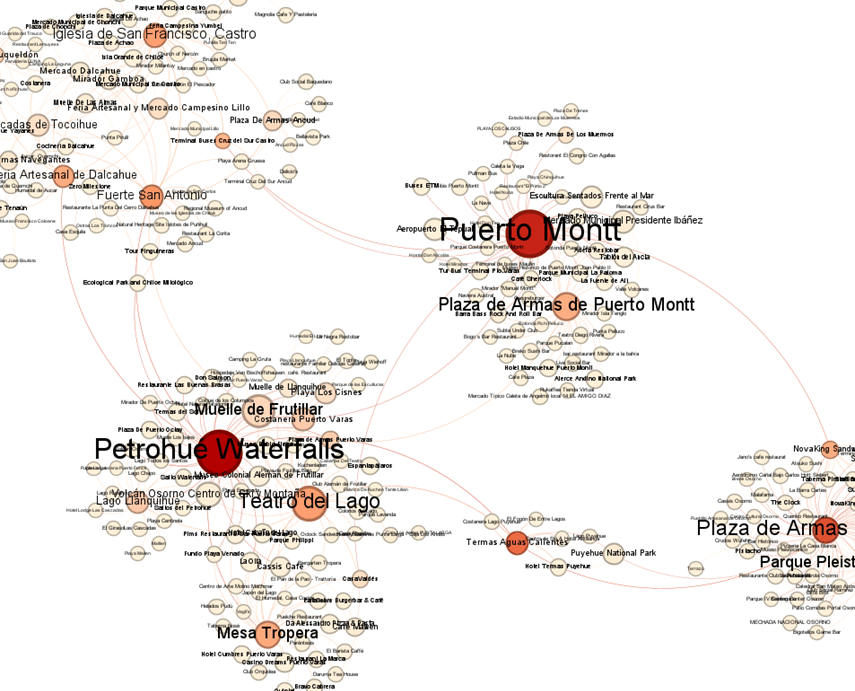
Development of a Content-Based Tourist Destination Recommendation System, designed as a digital public good leveraging Collective Intelligence. The system integrates Network Science, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Recommendation System techniques to map individual and collective preferences, democratizing access to complex data. A Graph Convolutional Neural Network (GCN) was implemented for edge prediction, capturing complex relationships between nodes and improving recommendation accuracy. Additionally, an Exponential Random Graph Model (ERGM) was used to explain link formation, providing insights into semantic and location similarity. This project proposes a ‘tourist space search’ as a digital public good that, through the application of network science, natural language processing, and recommendation systems, maps individual and collective user preferences. It highlights the richness of connections between heritage sites, natural landscapes, local gastronomy, and historic accommodations. The visualizations serve as a cognitive tool, allowing users to navigate the complexity of tourist data through a knowledge map that shows how different destinations are linked not by geographic proximity but by the affinity of experiences they offer. This project not only advances the way travelers interact with tourism information but also stands as a model for the development of digital public goods that promote culture and heritage through technology, democratizing access to tourism experiences.
Computer Vision
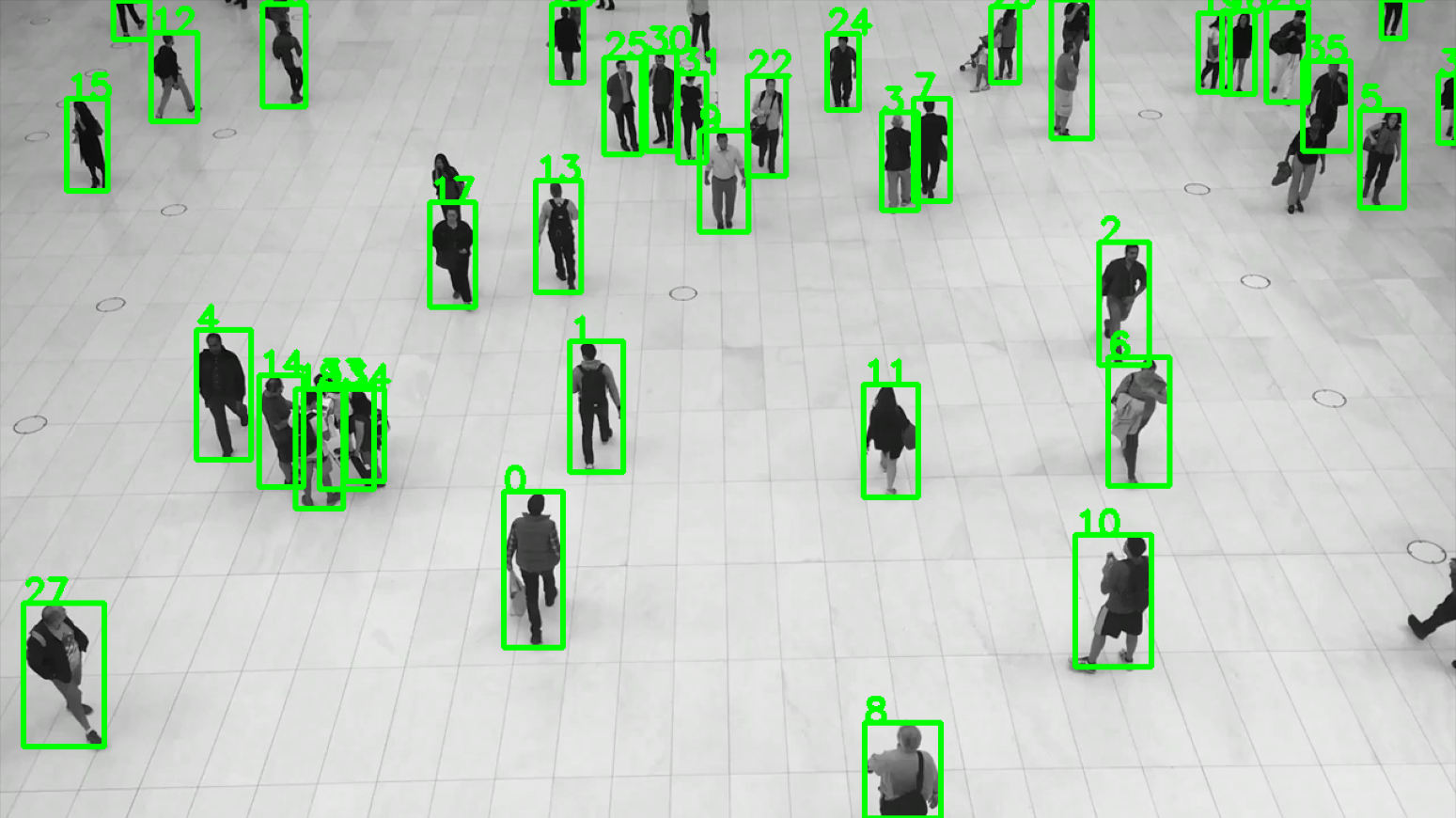
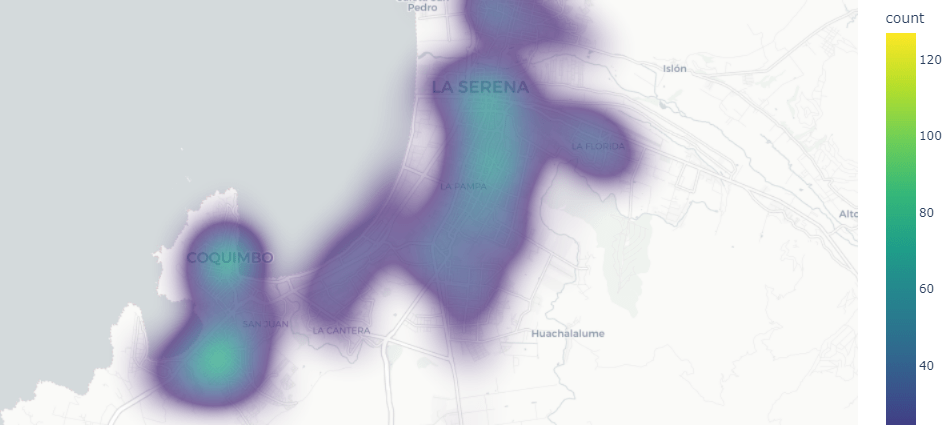
Using Object Tracking techniques to perform movement analytics and measure the proximity between people or the movement of people through areas of interest is a highly relevant problem. Optimizing the layout (product positioning) and generating heat maps that represent the flow of people provide important insights for decision-making. This information is useful to identify which areas are more frequented and have a higher flow of people, allowing the placement of higher-value products in those areas and/or reoptimizing the layout. This problem is transversal across multiple industries, from Retail and Shopping Malls to Casinos.




Geospatial Analytics
Geospatial analytics provides a global understanding of people, their needs, and behaviors within a given geographical environment, analyzing the economic and social reality from a geographic perspective through spatial statistical tools.


Neural Networks
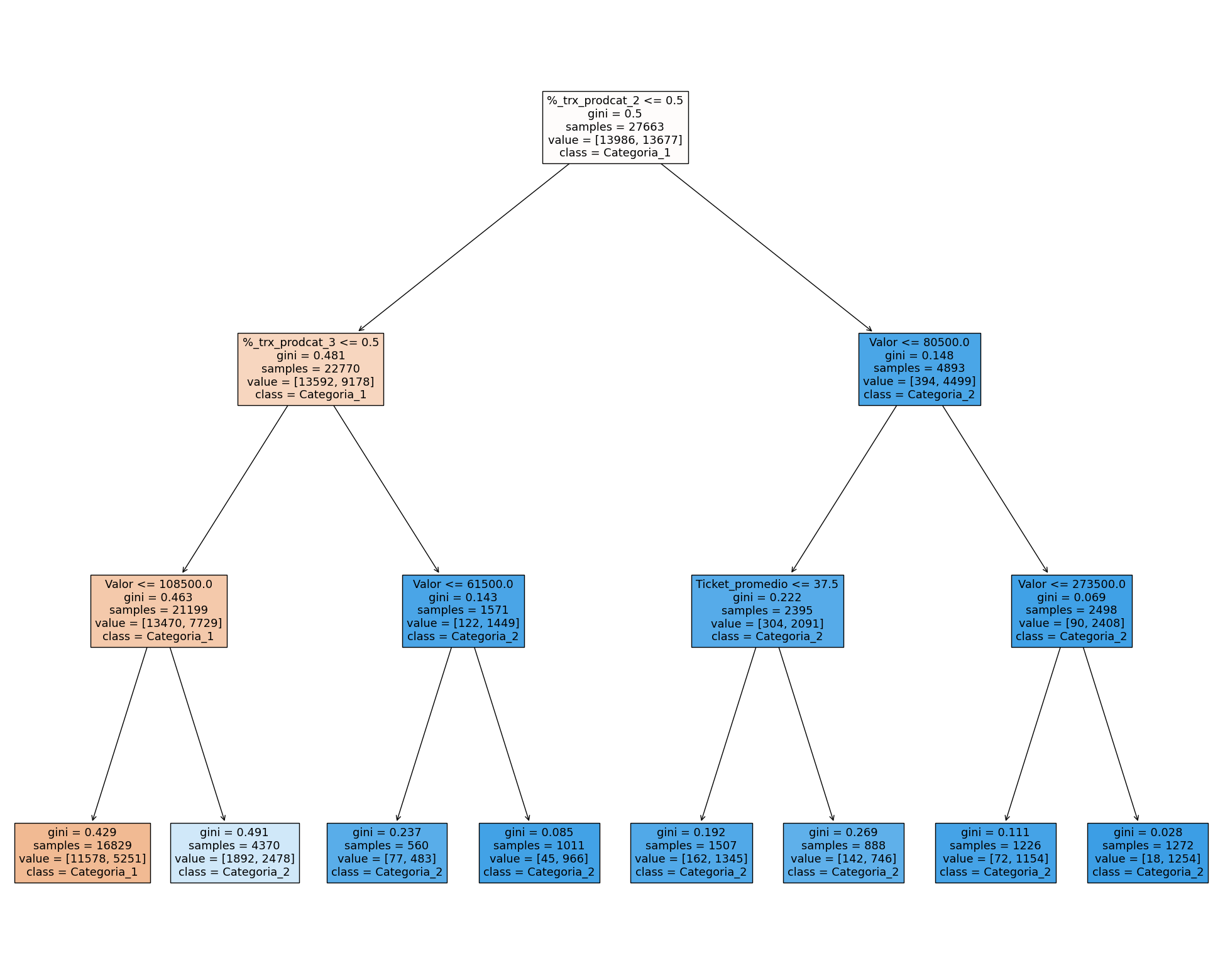
Artificial Neural Networks (NN) are mathematical models inspired by the functioning of the human brain, allowing them to capture complex patterns in large datasets. NNs have the ability to learn nonlinear and complex relationships from large datasets, making them efficient for classification and regression tasks. NNs, especially deep networks, are capable of working with heterogeneous data, such as images (CNN) or text (RNN, Transformer).


Algorithmic Explainability
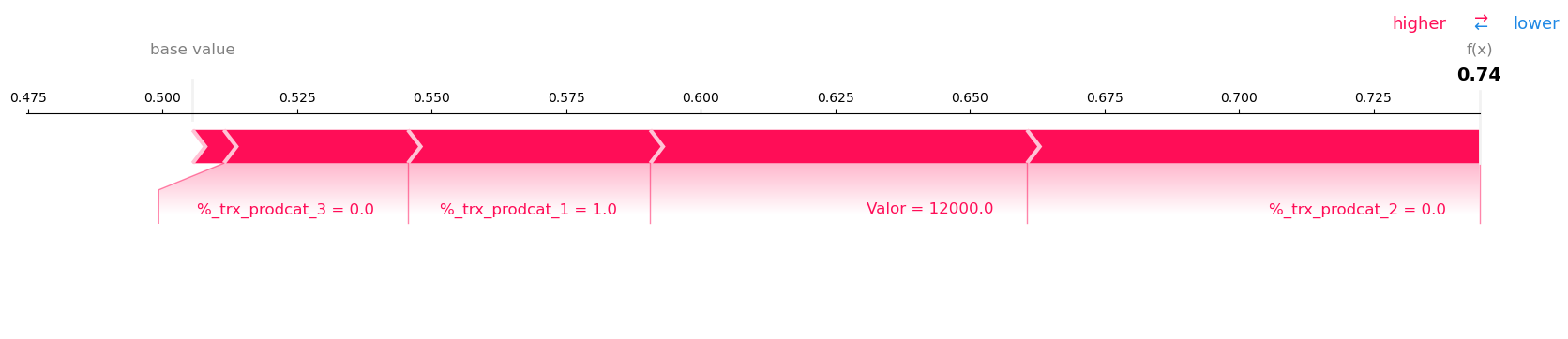
It is essential to understand and explain how artificial intelligence algorithms and models make decisions or generate predictions. As AI models become more complex, it becomes more difficult to understand the internal processes that lead to their outcomes. A relevant point is algorithmic transparency; it is crucial that data science projects are transparent and explainable. It is important to ensure there are no biases related to gender, ethnicity, religion, or any other factor that could lead to arbitrary discrimination, thereby avoiding the reproduction of societal stereotypes. Therefore, being able to explain which attributes are the most important, what the directionality is, and how much they influenced each decision is key to achieving algorithmic explainability and transparency.



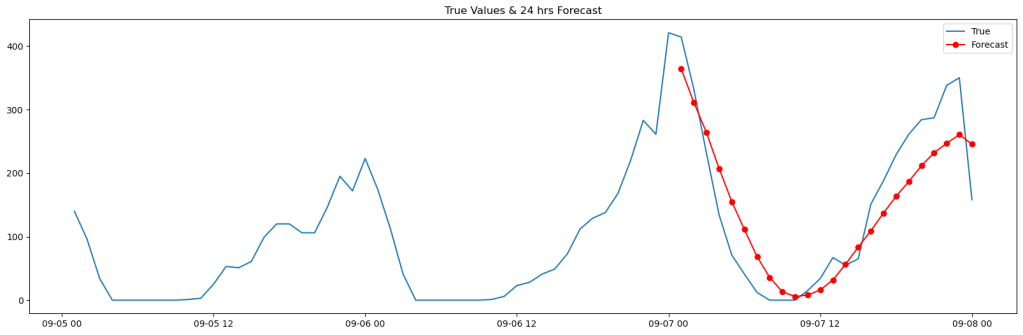
Forecasting
Forecast analysis is essential for understanding human behavior, allowing for the anticipation and prediction of future events, making informed decisions, and planning strategically. It helps in decision-making, supply chain management, production optimization, and improving customer satisfaction. By anticipating demand and planning appropriately, inventory issues can be avoided, costs minimized, and products can be ensured to be available when customers need them.

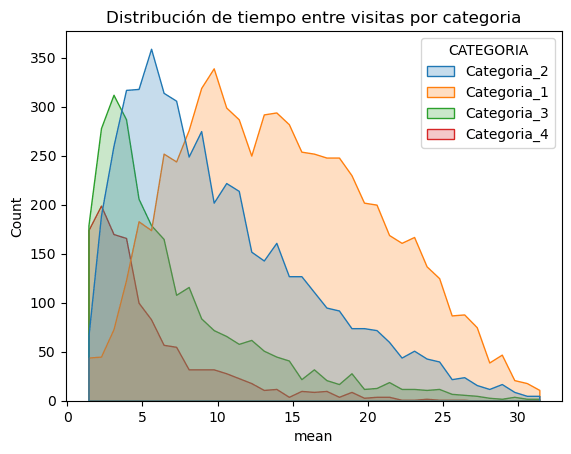
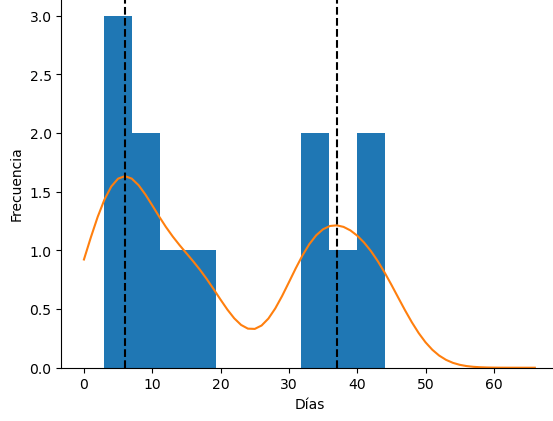
KDE
Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) is a statistical technique for estimating the probability distribution and helps to understand the time patterns between events. This method allows modeling behavior between visits with a visual representation of the distribution, identifying modes, peaks, and detecting anomalies. This knowledge is important for decision-making in Marketing and Commercial Strategy, as this information can be used as a predictive Churn model.